AI Agents Explained! Meet the Protagonists of the Digital Future
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Key Points
- AI agents are autonomous programs designed to perceive their environment, decide, and act to achieve specific goals [Reference 1].
- Their autonomy, ability to adapt, and goal orientation distinguish them from other AI systems [Reference 2].
- They can reason, learn from experience, and plan complex actions.
- Examples include personal assistants, customer service agents, and automated bots.
- Collaboration and the use of LLMs make them protagonists of the digital future.
Table of contents
Key concepts and features of AI agents
An AI agent is much more than a simple bot or software routine. They are entities capable of *perceiving*, *reasoning*, and *acting* to maximize their goals, adapting to the digital or physical environment and learning from experience.
- Autonomy: They operate without constant human supervision [1], [5].
- Perception and interaction: They sense from APIs, databases, or the web and interact with users or systems [3].
- Goal-oriented behavior: Their “actions” aim to maximize reward, utility, or adaptation functions [4].
- Adaptation and learning: They learn and improve their performance through feedback or machine learning [6].
- Reasoning and planning: They can sequence and execute complex actions in multiple steps [7].
- Collaboration: They work together with people or other agents, coordinating distributed processes [8].
- Types: From simple rule-based bots to sophisticated generative AI assistants [5].
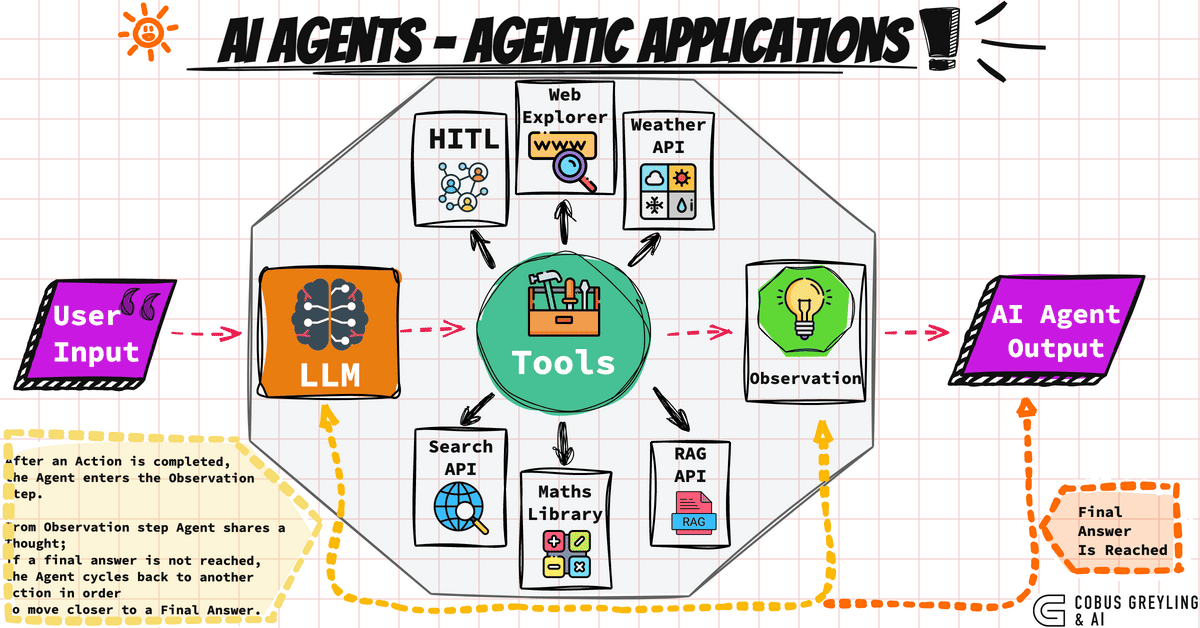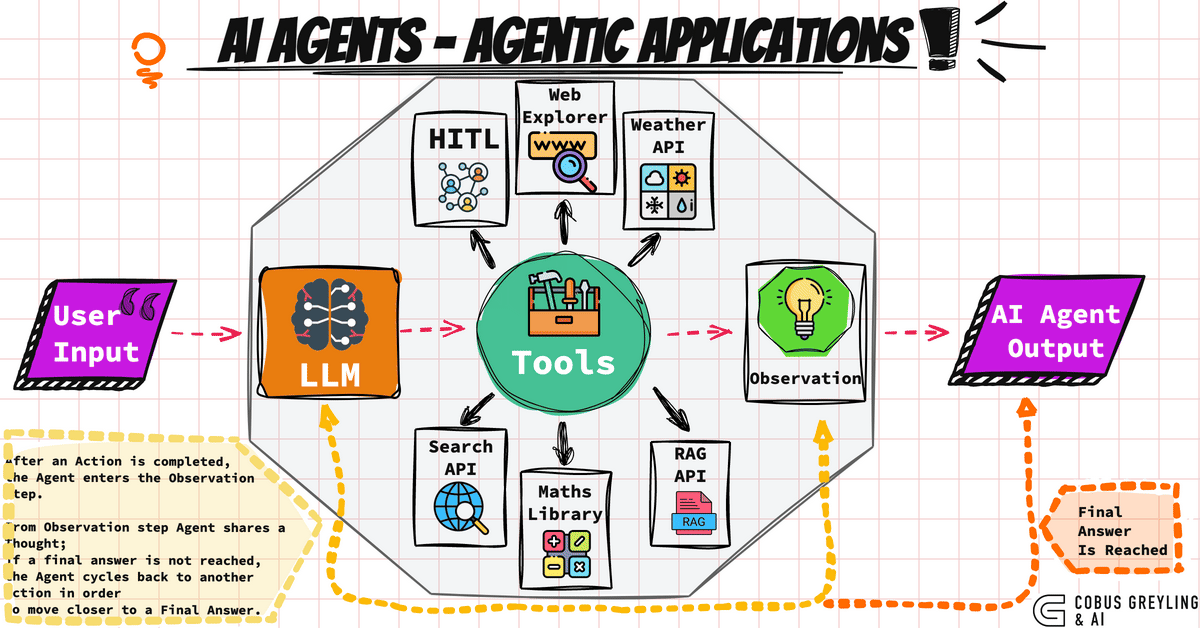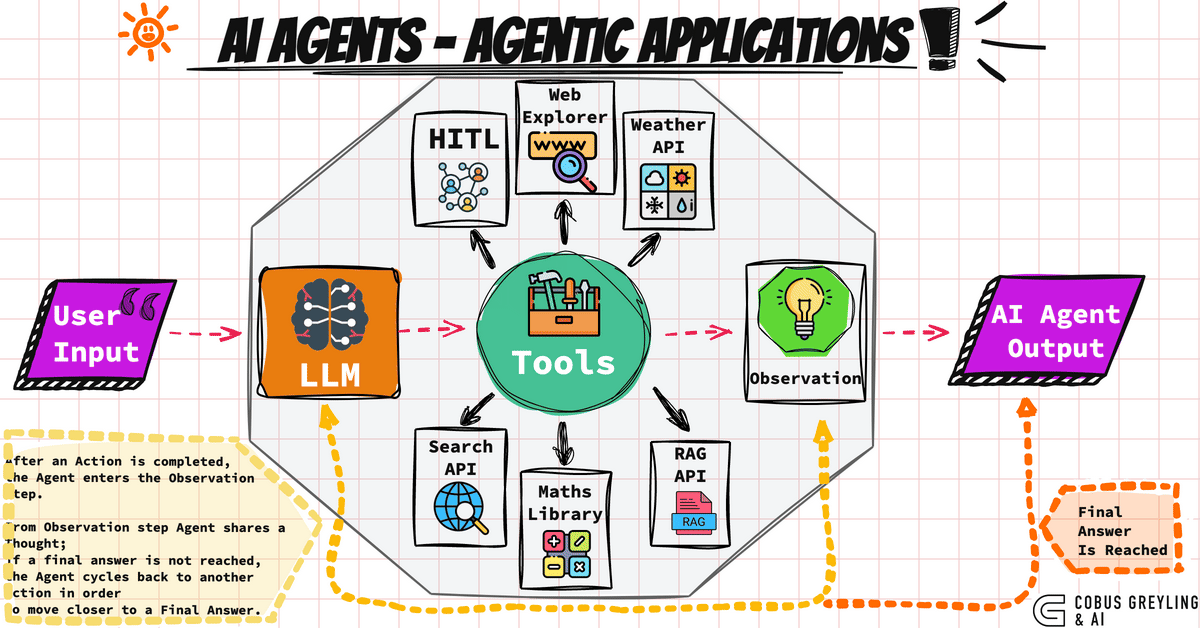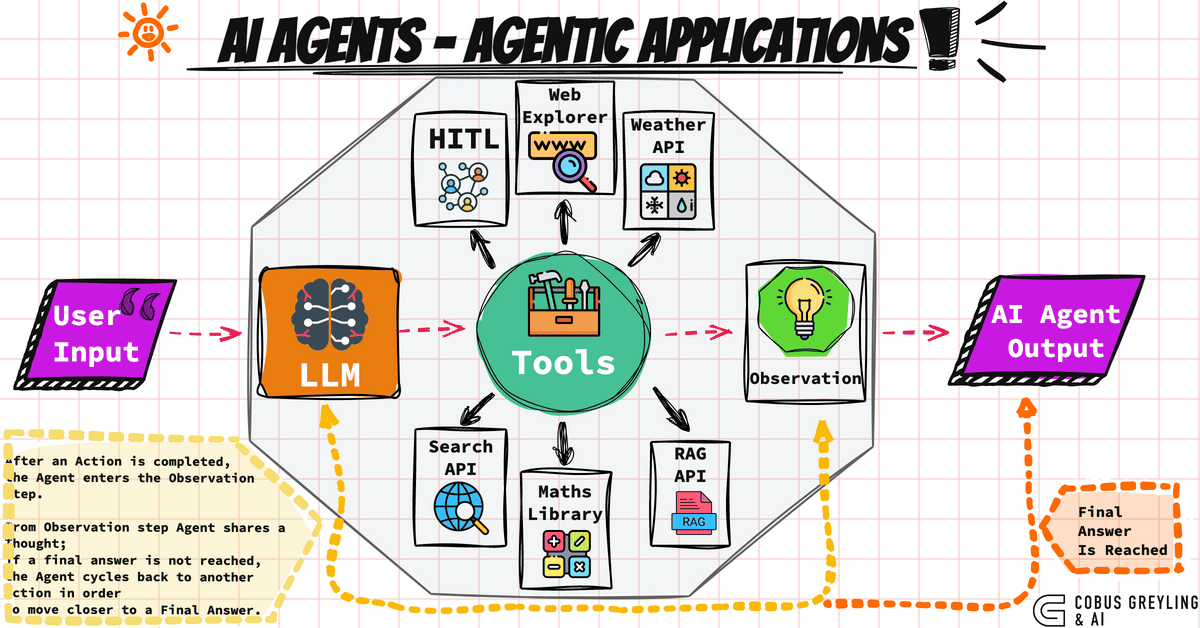
How do AI agents work?
The typical lifecycle of an AI agent consists of the following steps:
- Sensitization: They obtain and process information from their environment [1], [5].
- Decision: They reason and evaluate which action is the most appropriate according to data and objectives [4].
- Action: They perform tasks, send commands, interact with humans or APIs.
- Learning and adaptation: They adjust strategies thanks to the feedback received [6].
Examples of AI agents in action
- Customer service agents: They resolve questions, look for information, and propose solutions autonomously [3].
- Code assistants: Code suggestion, bug detection, and correction.
- Business agents: They automate flows such as billing, logistics, or human resources.
- AI personal assistants: They organize schedules, draft emails, and summarize information according to the user’s intent [5].
Technical bases and spectrum of autonomy
- Large Language Models (LLMs): The most advanced agents rely on models like GPT-4 to understand and converse in natural language [7].
- Use of APIs and tools: Access to databases, integration with external software, and coordinated action [5].
- Spectrum of autonomy: Some agents act completely autonomously; others are oriented to assist, collaborate, and learn from humans [8].
Comparison of types of agents
| Feature | Completely Autonomous Agent | AI Assistant | Simple Automation Bot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level of autonomy | High | Medium | Low |
| Task complexity | Multifaceted, reasoning | Simple to moderate | Rule-based, repetitive |
| Learning | Yes (often) | Sometimes | Rarely |
| User interaction | Predictive/Optional | Frequent, collaborative | Minimal, rule-based |
| Example | Self-driving | ChatGPT, Google Assistant | Email filter, FAQ bot |
In summary, *AI agents* are transforming the way we interact with technology, evolving from simple bots to complex collaborative systems. “Artificial intelligence will be as revolutionary as electricity,” according to experts in the field.
Frequently asked questions
-
What differentiates an AI agent from a simple bot?
A traditional bot executes tasks based on fixed rules and does not learn; AI agents are adaptive, make complex decisions, and can learn from past experiences.
-
Where are AI agents currently used?
In personal assistants, customer service, business automation, self-driving cars, and more [5].
-
Can AI agents replace humans?
They can automate repetitive tasks or analyze massive data, but human-machine collaboration remains essential for most scenarios [8].
-
What technologies power AI agents?
Language models (LLMs), machine learning, API integration and external software, and planning tools [7].